Circle buildings represent a groundbreaking architectural approach focused on sustainability, efficiency, and occupant well-being. Here are their ten most amazing features:
1. Optimized Thermal Performance
The circular form minimizes surface area relative to floor area, significantly reducing heat gain in summer and heat loss in winter. This creates a strong thermal buffer naturally.
2. Efficient Structural Design
Uniform load distribution around the circular perimeter allows for highly efficient material usage compared to rectilinear buildings, reducing embodied carbon.
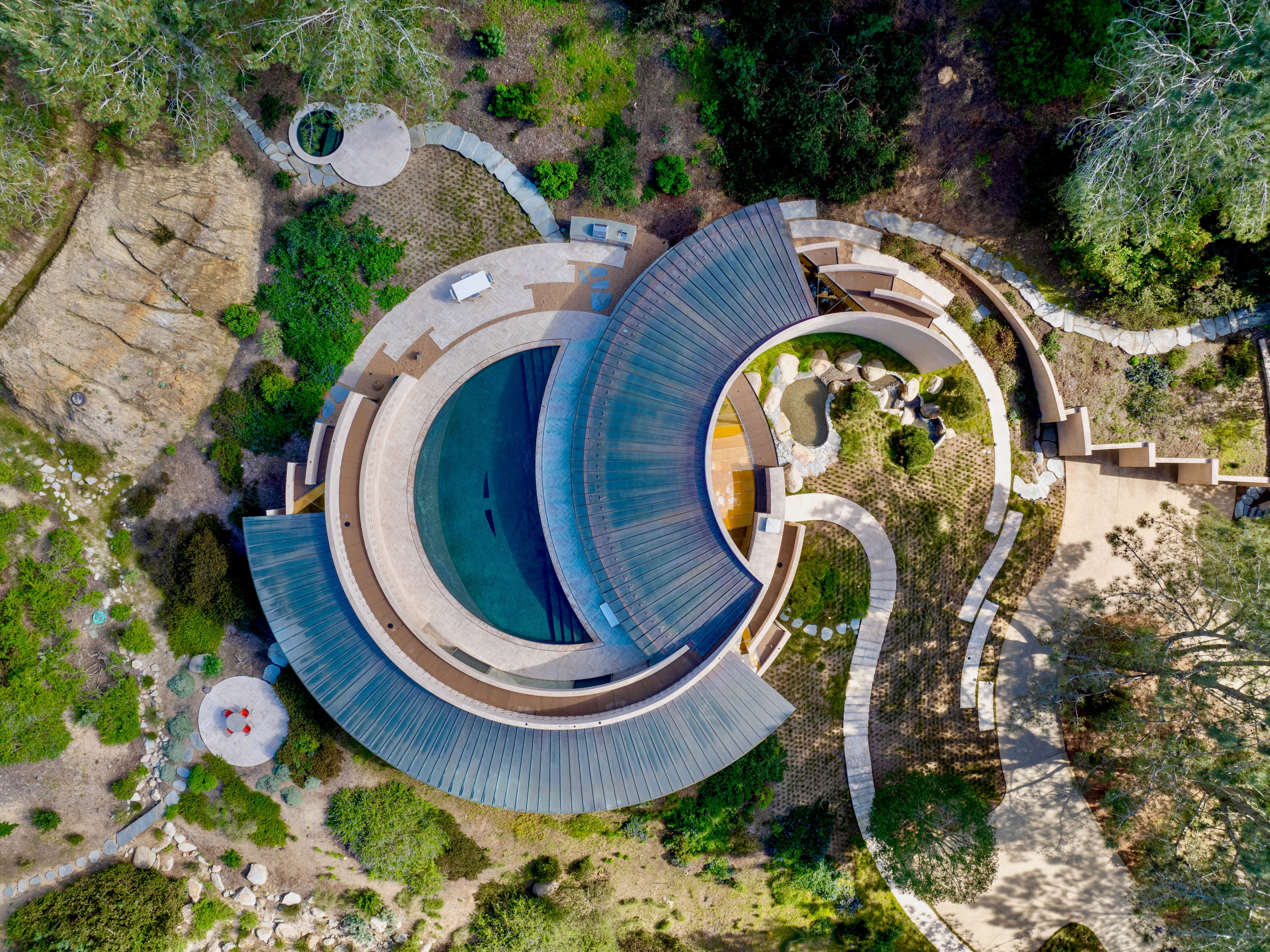

3. Enhanced Natural Ventilation
Aerodynamic shapes facilitate superior cross-ventilation patterns. Strategic window placement capitalizes on prevailing winds for passive cooling throughout interior spaces.
4. Optimal Daylight Harvesting
A central atrium, common in many circle designs, acts as a giant light well. Combined with perimeter glazing, this ensures deep daylight penetration, reducing reliance on artificial lighting.
5. Minimal Wind Load Impact
The absence of sharp corners dramatically reduces wind pressure differentials, lowering structural requirements and associated costs while improving occupant comfort.
6. Regenerative Energy Potential
The expansive, often unbroken roof surface provides significant area for solar photovoltaic arrays or green roofing systems, enabling high on-site renewable energy generation.
7. Superior Structural Resilience
The continuous load path inherent in circular structures offers increased resistance to lateral forces, such as earthquakes and high winds, enhancing building safety.
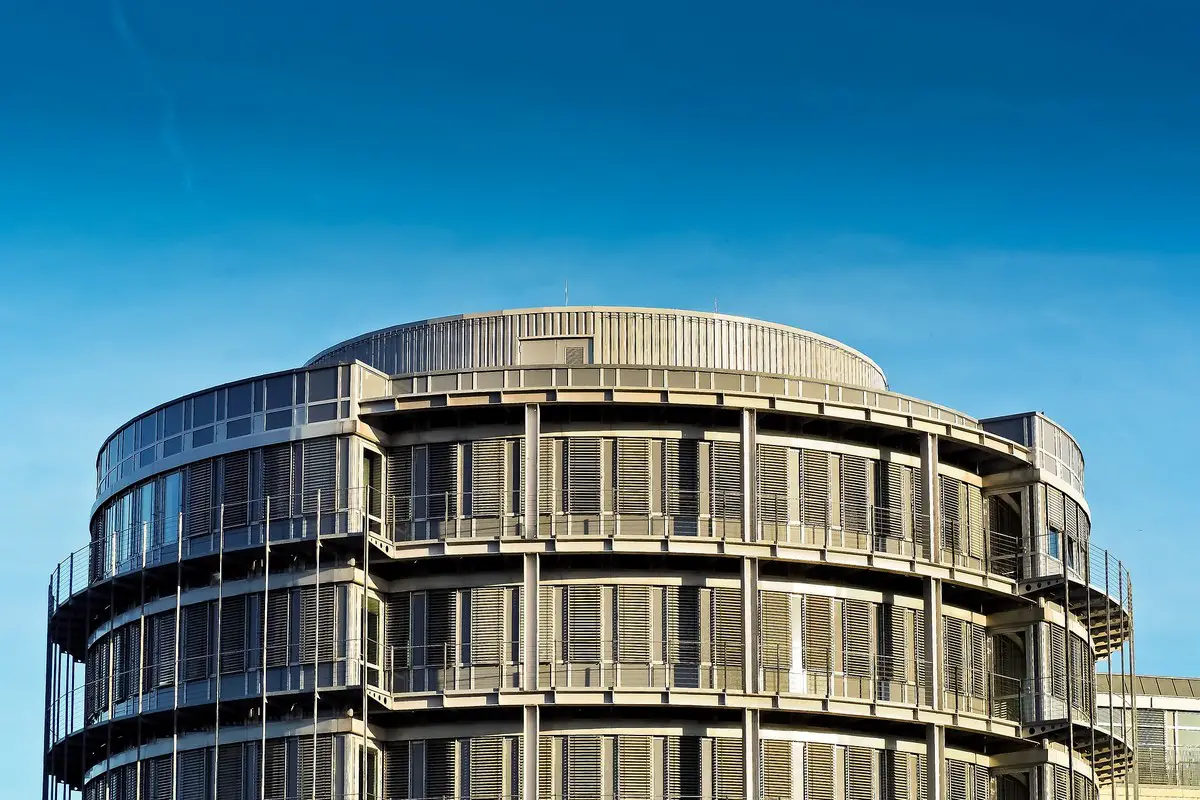

8. Efficient Space Utilization
Eliminating internal corners minimizes unusable space, leading to highly efficient floor plans and potentially higher net-to-gross area ratios compared to traditional designs.
9. Integrated Mixed-Use Functionality
Circular forms readily accommodate diverse programmatic zones around a central core or atrium, fostering vibrant, interconnected communities within a single structure.
10. Advanced Data-Driven Optimization
The geometric simplicity facilitates sophisticated computational modeling for optimizing energy flows (light, air, heat), material performance, and occupant spatial analytics.