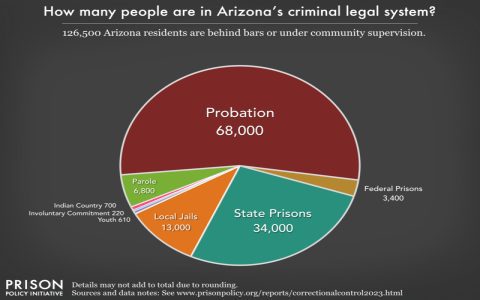
Anstalten Prisons are penal institutions primarily in German-speaking countries like Germany, Austria, and Switzerland, serving as facilities for incarcerating individuals convicted of crimes. They form a key component of the correctional system, focusing on the secure confinement and resocialization of offenders.
Core Functions
The primary functions of Anstalten Prisons include:
- Secure Confinement: Ensuring the safety of inmates and society through controlled environments, which may range from high-security for dangerous offenders to open institutions for low-risk individuals.
- Rehabilitation and Resocialization: Providing programs such as education, vocational training, therapy, and work assignments to prepare inmates for successful reintegration into society.
- Punitive Measures: Enforcing court-imposed sentences while upholding legal standards to maintain accountability for criminal acts.
- Societal Protection: Reducing public risk by isolating offenders and implementing preventive security protocols.
- Medical and Psychological Care: Offering essential healthcare and mental health services to address inmates' well-being and reduce recidivism.
Operational Characteristics
- Administration: Managed by state justice departments, with oversight to comply with national laws such as Germany's Strafvollzugsgesetz (Penal Execution Act).
- Inmate Classification: Sorting prisoners based on risk levels, sentence length, and personal needs to optimize supervision and program effectiveness.
- Facility Types: Differentiated into categories like closed prisons for high-security needs and open prisons emphasizing trust and community-based resocialization.
- Program Implementation: Conducting regular evaluations to adapt rehabilitative strategies and ensure human rights adherence.