Contemporary architectural trends increasingly prioritize sustainable, adaptive, and human-centric solutions. Key patterns shaping modern construction include:
Sustainable Material Integration
The shift towards low-carbon and circular materials is paramount. Mass Timber (CLT, Glulam) offers structural strength with significant carbon sequestration benefits. Recycled steel, low-carbon concrete mixes, and bio-based materials like mycelium insulation are gaining traction, reducing embodied energy and promoting resource efficiency.
Biophilic and Wellness-Oriented Design
Integrating nature to enhance occupant well-being is a core principle. This involves:
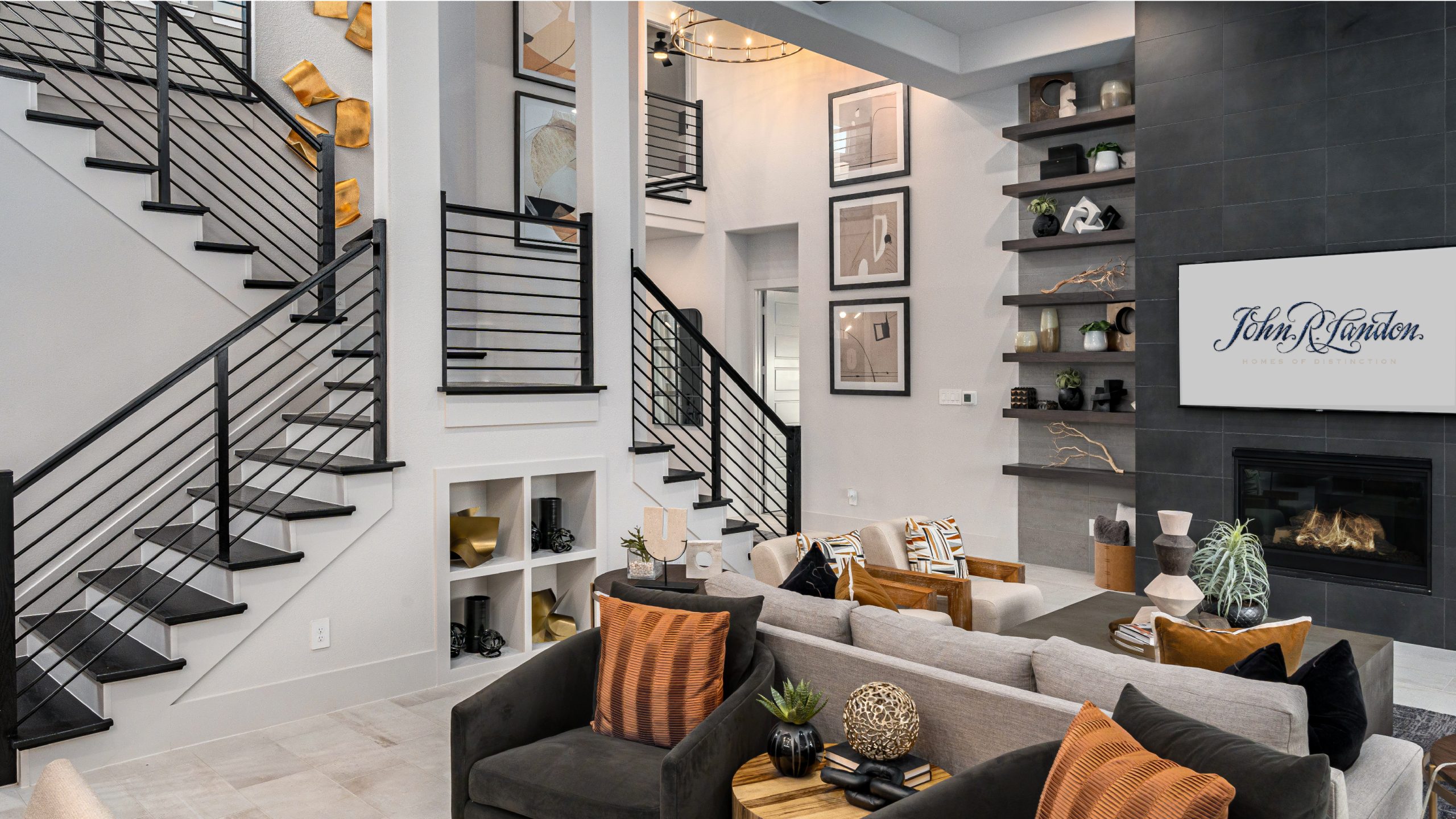

- Optimized Natural Light: Maximizing daylight penetration with larger windows, light shelves, and strategically placed atria.
- Living Walls & Indoor Greenery: Improving air quality, thermal regulation, and psychological well-being.
- Natural Material Palette: Using wood, stone, and textiles to create calming, tactile environments.
Adaptive Reuse & Flexibility
Re-purposing existing structures reduces waste and preserves cultural heritage. Designing for flexibility—using demountable partitions, modular components, and adaptable MEP systems—ensures buildings can evolve with changing user needs, extending lifespan and minimizing obsolescence.
Prefabrication & Modular Construction
Off-site manufacturing accelerates project timelines, enhances precision, reduces waste, and improves safety. Modern techniques, including advanced BIM integration and robotic assembly, are enabling more complex and higher-quality prefabricated elements.
Energy Autonomy & Smart Technologies
Buildings are moving towards net-zero or positive energy contributions:
- Advanced Envelopes: High-performance facades with dynamic shading and optimized insulation.
- Renewable Integration: Seamless incorporation of solar PV, geothermal systems, and wind energy.
- AI-Driven Building Management: Systems continuously monitor and optimize energy use, indoor air quality, lighting, and thermal comfort.
Resilience & Climate Adaptation
Design incorporates strategies to withstand and adapt to changing climate conditions: robust waterproofing, flood-resistant foundations, passive survivability features for power outages, elevated mechanical systems, and consideration for future climate loads.
Collectively, these patterns drive an industry transformation towards greater environmental responsibility, occupant health, technological integration, and long-term value.