Structural Design Principles
Engineers designing Chinese glass bridges focus on robust structural integrity to support dynamic loads from visitors and environmental stressors like wind and seismic activity. Calculations include finite element analysis to distribute weight evenly across the bridge, ensuring deflection remains within strict safety tolerances of less than 1/1000 of the span.
For height adaptation, designers utilize reinforced concrete foundations anchored deep into bedrock, combined with lightweight steel frameworks optimized for strength-to-weight ratios. Wind tunnel testing models potential resonance frequencies to incorporate damping systems that minimize vibrations.
Material Selection and Safety
Laminated glass panels, typically comprising three to five layers of tempered glass bonded with polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayers, form the core safety feature. This configuration prevents shattering and maintains integrity under impact loads exceeding 500 kg per panel.
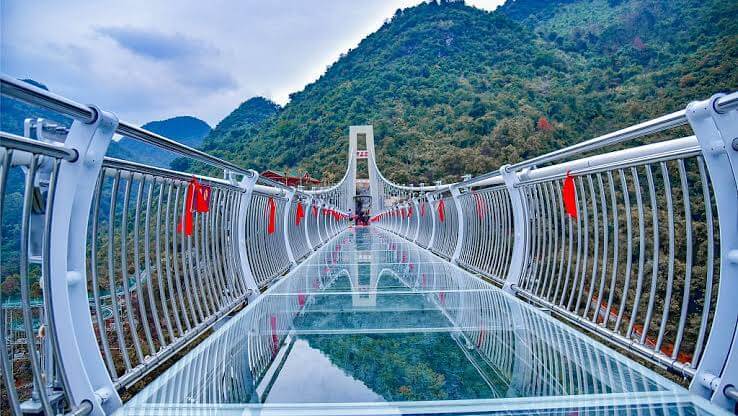

- Load Distribution: Panels are engineered to redistribute localized pressure, utilizing bolted joints to the structural frame.
- Resistance Testing: Bridges undergo rigorous simulated load tests with weights up to design limits, followed by cyclic fatigue assessments to certify 100-year lifespans.
Construction Process
Site selection prioritizes stable geology, avoiding fault lines through geological surveys. Construction begins with excavating and pouring reinforced foundations, setting pre-fabricated steel supports via cranes, and attaching glass panels in stages.
- Foundation Phase: Drilling piles to depths of 30-50 meters ensures stability on mountainous terrain.
- Glass Installation: Automated cranes place panels with millimeter precision using shock-absorbing mounts to avoid stress concentrations.
- Final Integration: Sealing edges with specialized silicone prevents moisture ingress and thermal expansion issues.
Safety and Maintenance Protocols
Post-construction, bridges incorporate real-time structural health monitoring systems with sensors detecting stress anomalies. Regular inspections enforce daily visual checks and bi-annual ultrasonic testing for micro-cracks.
Emergency plans include evacuation routes and redundant supports, while non-slip glass surfaces reduce slip risks. Safety standards align with Chinese national codes GB 50017 and ISO 22111.