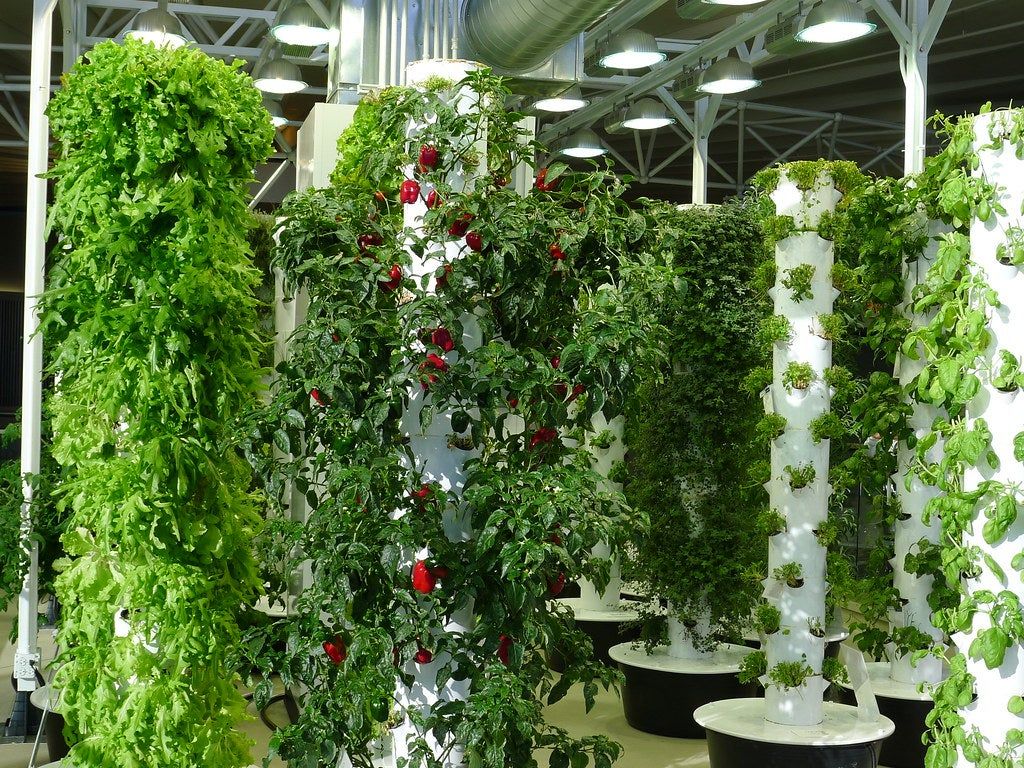
A farm tower, also referred to as a vertical farm or plant tower, is an agricultural system designed for growing crops in vertically stacked layers, integrated structures, or towers. This method is a prominent example of Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA), aiming to optimize plant growth conditions and resource utilization.
Core Concepts and Technologies
Farm towers leverage several key technologies and principles to achieve efficient food production:
- Vertical Stacking: Maximizes crop output per unit of land area by utilizing vertical space. This is particularly advantageous in urban settings or areas with limited arable land.
- Soilless Cultivation Methods:
- Hydroponics: Plants are grown with their roots submerged in a nutrient-rich water solution.
- Aeroponics: Plant roots are suspended in the air and misted with a nutrient-dense solution. This method often uses less water and nutrients than hydroponics.
- Aquaponics: An integrated system combining aquaculture (raising aquatic animals like fish) with hydroponics. Fish waste provides nutrients for the plants, and plants filter the water for the fish.
- Controlled Environment: All critical environmental factors are meticulously managed. This includes:
- Lighting: Often utilizes artificial light sources, primarily LED grow lights, tailored to specific plant needs for photosynthesis.
- Temperature and Humidity: HVAC systems maintain optimal atmospheric conditions.
- CO2 Levels: Carbon dioxide levels can be enriched to enhance plant growth.
- Nutrient Management: Precise delivery of essential minerals to plants.
- Automation and Monitoring: Sensors and automated systems are often employed to monitor environmental conditions, deliver water and nutrients, and adjust lighting, reducing manual labor and ensuring consistency.
Advantages of Farm Towers
- Increased Crop Yield: Significantly higher productivity per square foot compared to traditional outdoor farming.
- Reduced Water Consumption: Recirculating water systems can decrease water usage by up to 90-95%.
- Year-Round Production: Independent of external weather patterns, enabling continuous harvests throughout the year.
- Minimized Pesticide and Herbicide Use: The controlled and often enclosed environment reduces pest and disease pressure, often eliminating the need for chemical interventions.
- Reduced Transportation Costs: Can be located in or near urban centers, shortening supply chains, reducing food miles, and delivering fresher produce.
- Land Use Efficiency: Requires substantially less land compared to conventional agriculture.
Challenges and Considerations
- High Initial Capital Costs: Significant upfront investment is required for infrastructure, technology, and setup.
- Energy Consumption: Artificial lighting and climate control systems can be energy-intensive. However, advancements in LED technology and renewable energy integration are helping to mitigate this.
- Technical Expertise: Operating and maintaining a farm tower requires specialized knowledge in plant science, engineering, and data management.
- Limited Crop Variety: While expanding, the technology is currently most economically viable for leafy greens, herbs, microgreens, and some vining fruits like strawberries and tomatoes. Staple crops are generally not yet feasible.
- System Complexity: Sophisticated systems can be prone to technical failures if not properly managed.
Farm towers represent a rapidly evolving field in agriculture, offering a promising solution for sustainable food production, particularly in resource-limited environments and urban areas. They contribute to food security, reduce environmental impact, and provide consumers with locally grown, fresh produce.