Selecting architectural stairs involves key factors for safety, function, and aesthetics. Focus on fundamental aspects tailored to beginners' projects.
Material Selection
Choose materials based on durability, maintenance, and building style:
- Wood: Classic for residential interiors; affordable but requires sealing.
- Metal: Ideal for modern designs; robust but needs rust prevention.
- Concrete: Suited for high-traffic areas; durable but costly.
Space and Dimensions
Ensure stair proportions meet ergonomic standards:
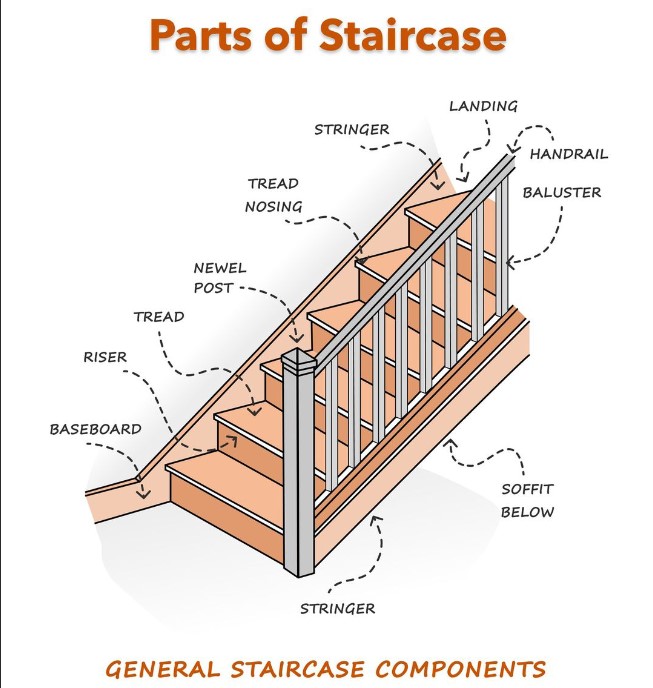
- Riser height: Aim for 150-200 mm; avoid extremes for comfort.
- Tread depth: Minimum 225 mm; deeper for public spaces.
- Clearance: Provide headroom ≥ 2000 mm; width ≥ 900 mm for flow.
Functionality and Use
Define stair purpose and flow:
- Type: Opt for straight runs in limited spaces; spirals save floor area.
- Traffic: Wider stairs (≥1000 mm) for commercial; consider landings every 12-18 risers.
Aesthetic Integration
Match stairs to architectural style:
- Design: Floating treads for contemporary; panelized for traditional.
- Finish: Coordinate colors and textures; ensure handrail alignment.
Codes and Safety
Prioritize compliance and hazard prevention:
- Building regulations: Check local codes like ADA or EN norms.
- Safety features: Install slip-resistant surfaces; handrails at 900-1000 mm height.