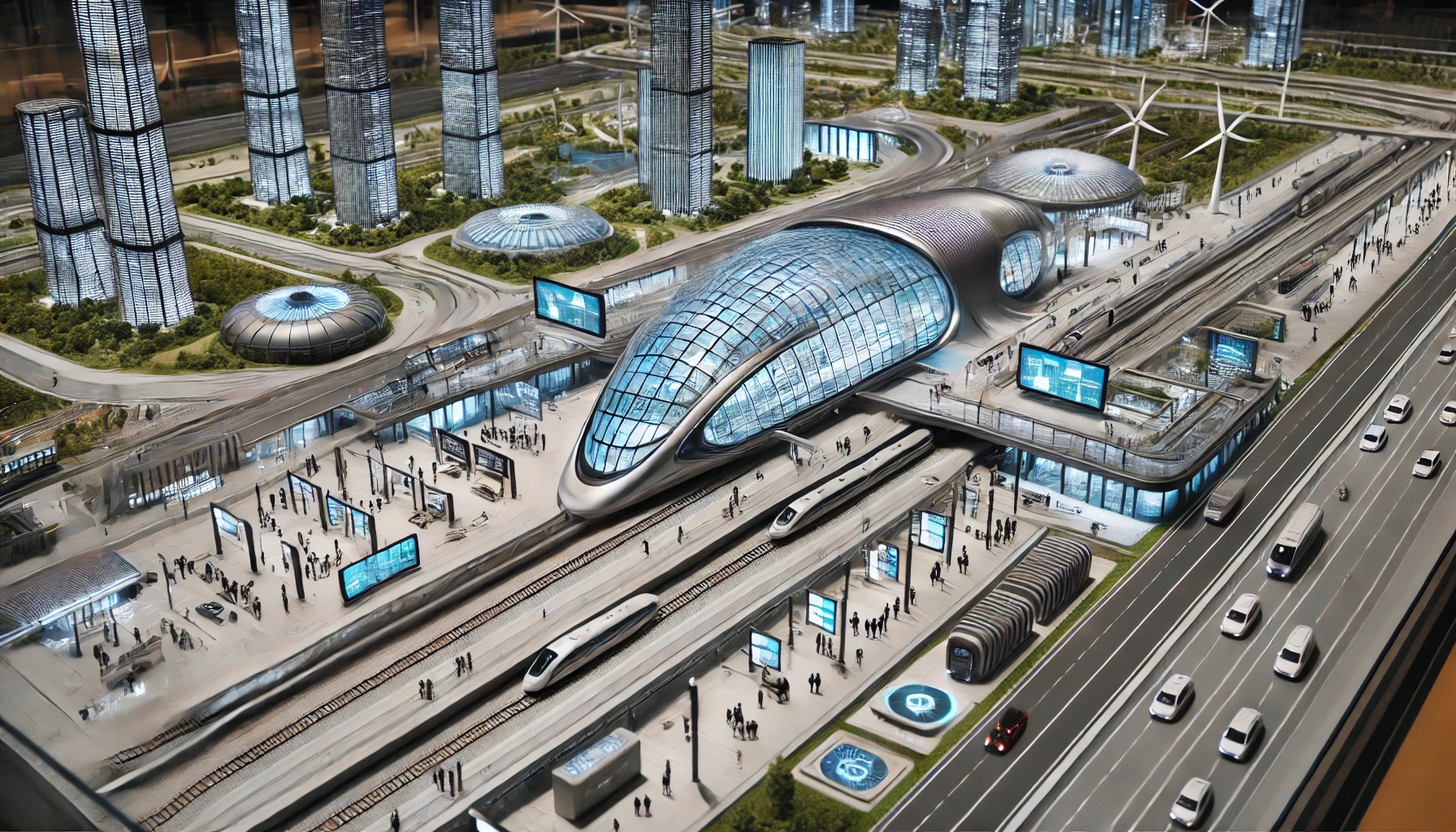
Future railway stations are evolving into multimodal urban hubs, integrating sustainability, technology, and passenger-centric design. Here are key concepts defining next-generation stations:
Multimodal Integration Hubs
Stations transcend traditional rail functions to become central interchange points. They seamlessly integrate high-speed rail, regional trains, metros, buses, cycling networks, and future transport like eVTOL air taxis. Dedicated lanes and priority systems optimize traffic flow. Co-location of services maximizes accessibility.
Energy-Positive Infrastructure
Design leverages renewable energy generation:
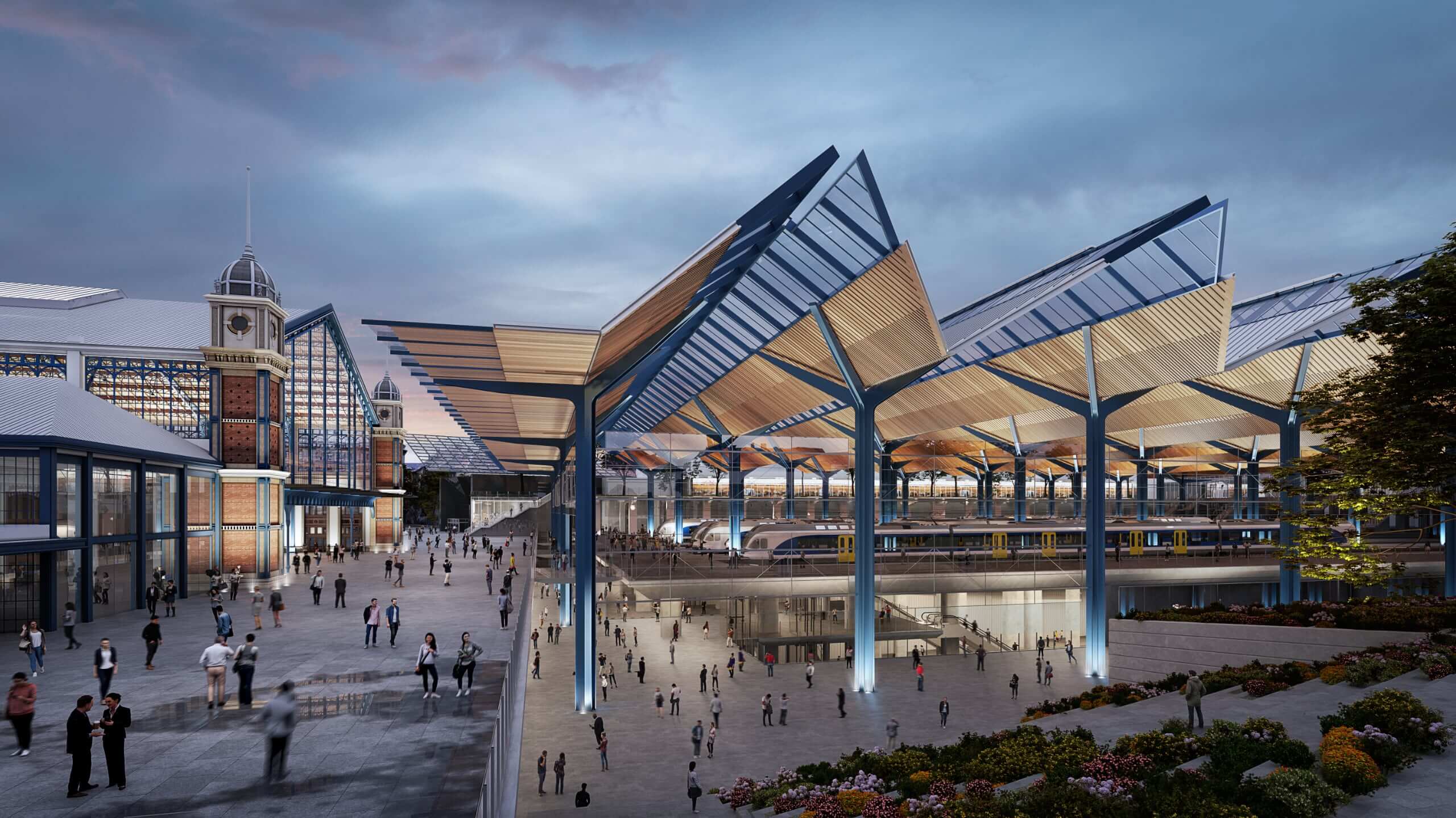

- Photovoltaic Integration: Canopies, facades, and roofs incorporate high-efficiency solar panels.
- Geothermal Systems: Utilizes subsurface thermal energy for heating and cooling.
- Kinetic Harvesting: Floors capture energy from passenger movement.
- Smart Grids: Stations act as local energy nodes, managing storage (batteries) and distribution.
Hyper-Personalized Passenger Experience
Technology anticipates and caters to individual needs:
- AI-Driven Navigation: Real-time, personalized wayfinding via apps and interactive signage adapts to disruptions.
- Biometric Travel: Frictionless access, security, and payment systems streamline journeys.
- On-Demand Services: Automated retail, luggage handling, and micro-mobility options are accessible instantly.
- Flexible Spaces: Configurable zones accommodate remote work, leisure, or quiet retreats.
Advanced Digital Twin Management
Virtual replicas optimize operations and maintenance:
- Real-Time Monitoring: IoT sensors track structural health, crowd density, energy use, and environmental conditions.
- Predictive Analytics: AI anticipates maintenance needs, crowd surges, and potential failures.
- Simulation Testing: Operators model responses to emergencies or schedule changes in the virtual environment.
Adaptive & Regenerative Architecture
Buildings are designed for longevity and minimal environmental impact:
- Modular Construction: Prefabricated components enable faster building and future reconfiguration.
- Circular Materials: Use of recycled, upcycled, and bio-based materials reduces embodied carbon.
- Green Infrastructure: Extensive green roofs, vertical gardens, and integrated water management enhance biodiversity, air quality, and passenger well-being.
Logistics & Automated Cargo Integration
Stations efficiently handle passenger and freight flows:
- Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): Underground tunnels or dedicated decks manage parcel and goods transfer independently.
- Multi-Level Sorting: Compact automated systems utilize vertical space for efficient logistics.
- Urban Consolidation: Stations become critical nodes for last-mile delivery, reducing road congestion.
The future station transforms from a transit point into a responsive, sustainable, and experience-focused urban nexus, leveraging technology to enhance connectivity and resilience.